BIND 9.20 Resolver performance compared to 9.18
In this post, we will show that BIND 9.20 compares favorably with 9.
Read postStork 1.13 is the newest development release of our management tool for the Kea DHCP server. Stork is open source, licensed under the MPL 2.0 license. A single Stork server works with Stork agent probes deployed on each of your Kea servers to provide monitoring, including details of the software versions installed, CPU and memory usage, high-availability pairing and status, as well as detailed traffic and activity statistics on leases, DORAs, NAKed offers and so on.
With this release, Stork is really no longer just a dashboard and monitoring tool. Stork can now provide meaningful configuration control, over not just one Kea server, but your entire deployment of multiple Kea servers.
Subnet configuration is one of the more complex, and error-prone areas of configuration, and one where there is a high likelihood that multiple Kea servers may be able to share configuration information. Most Kea users have configured their servers in a high-availability pair configuration, and a subnet which might be served by either Kea instance will need to be configured on both machines. This is why subnet configuration is the focus for Stork’s initial Kea configuration capabilities.
Stork provides a detailed list of all subnets configured in the managed Kea servers, with their local subnet identifiers. Different Kea servers may use different identifiers for the same subnet.
Usage statistics by subnet are is shown in pie charts.
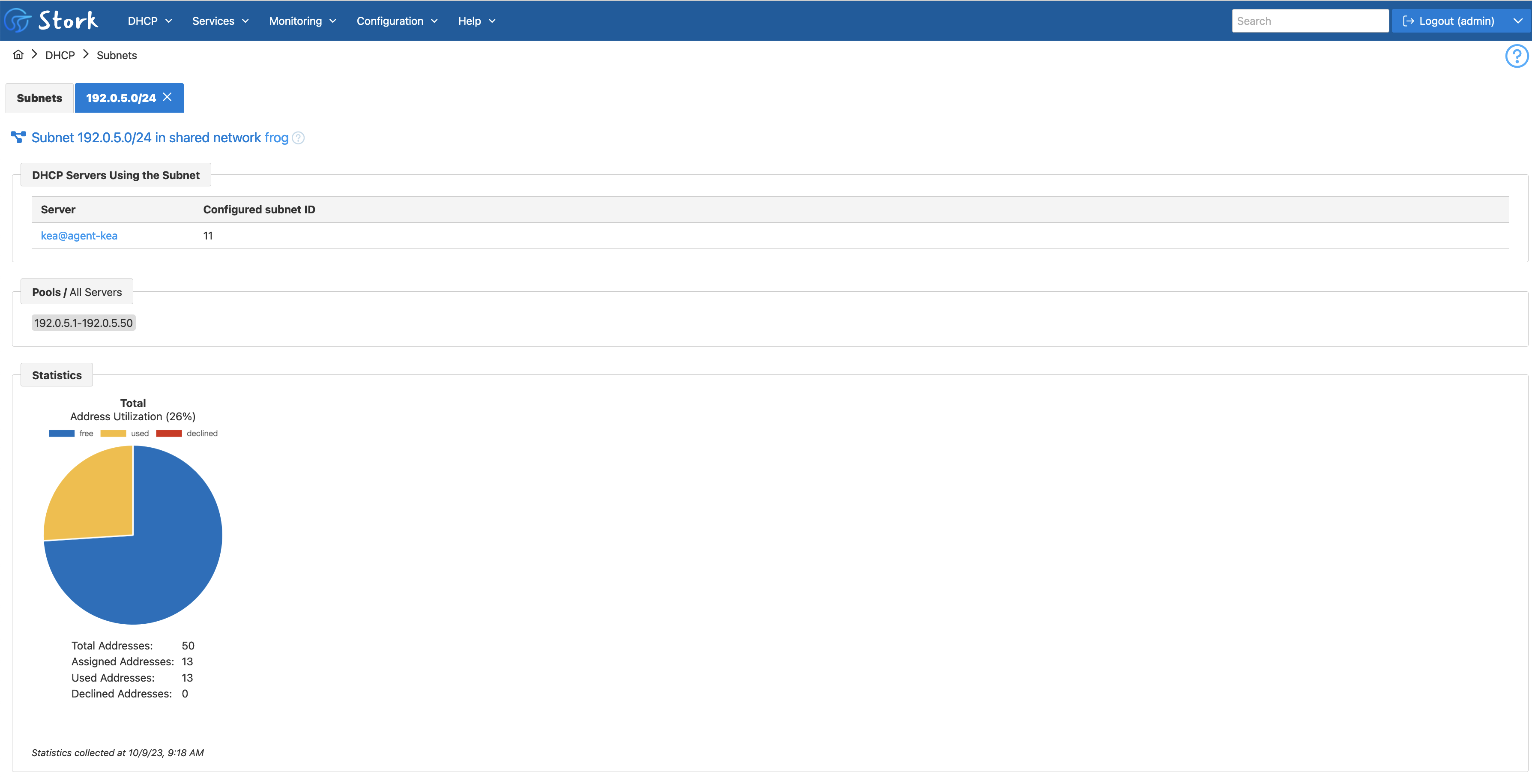
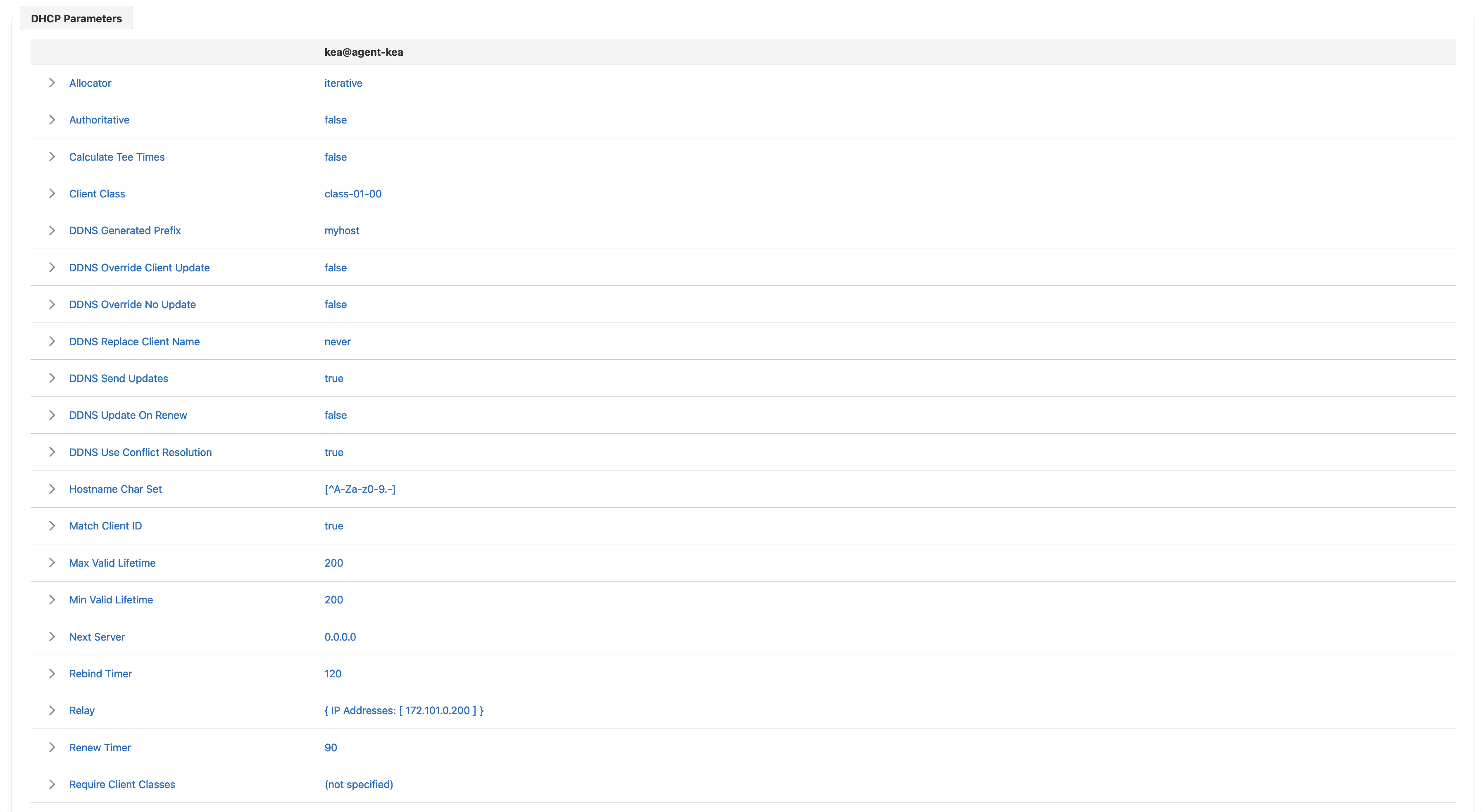
Expandable rows display the values of the various DHCP parameters specified at different configuration levels (i.e., subnet, shared network, and global level).
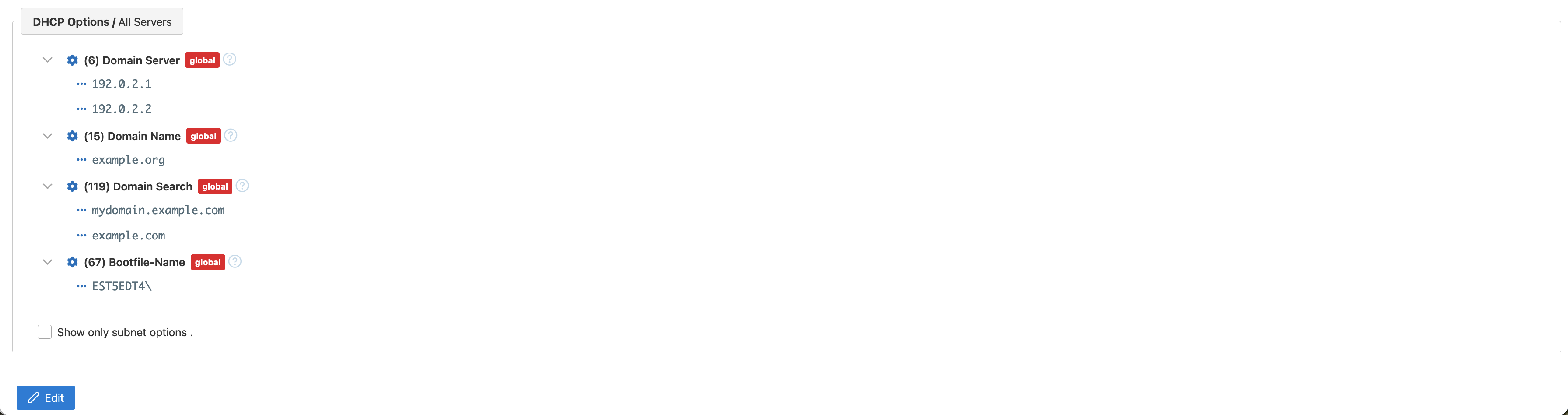
Finally, the subnet view contains DHCP options specified for the subnet at different levels (i.e., subnet, shared network, and global level). The checkbox allows for filtering to display only subnet-level options.
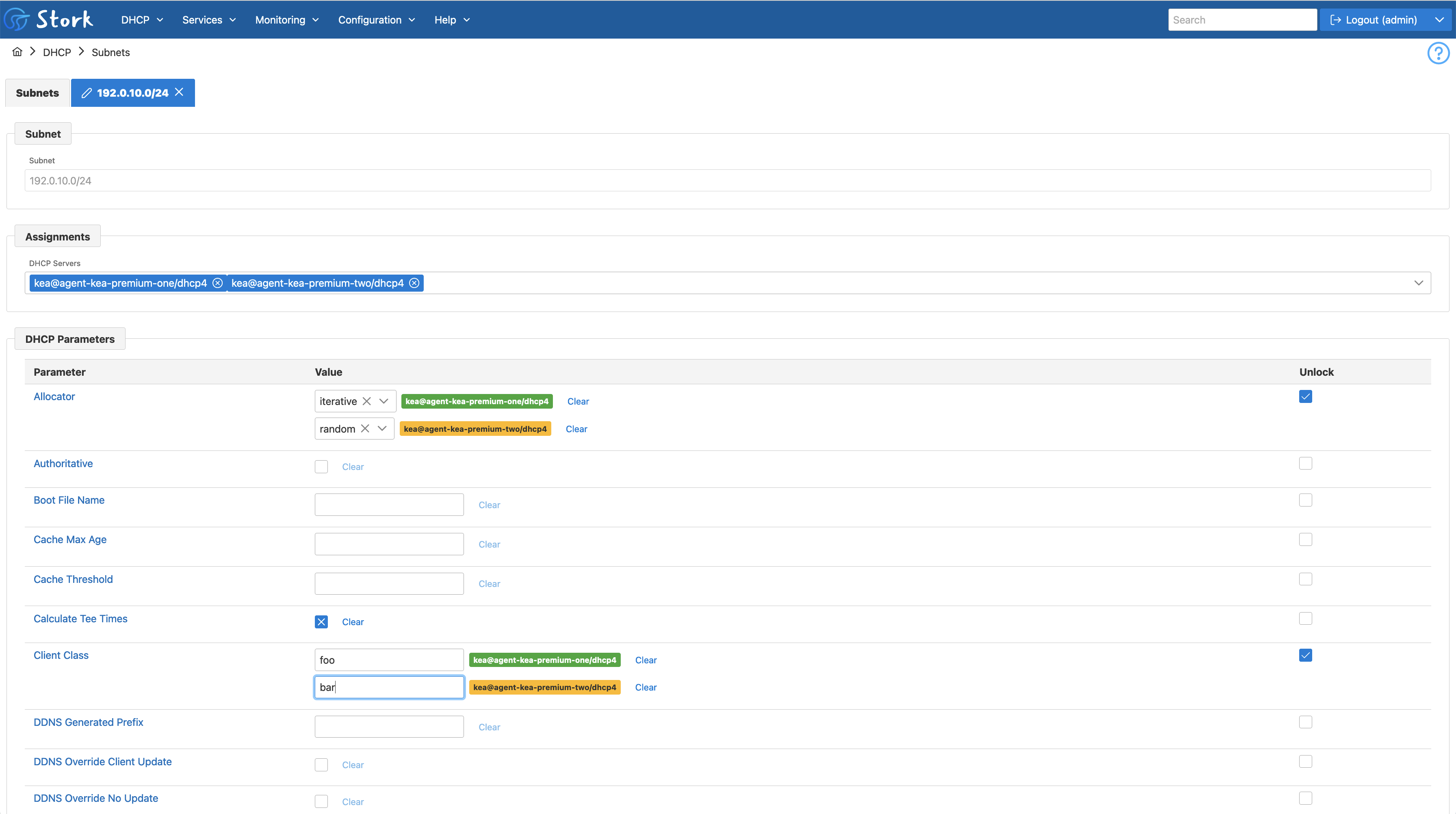
Stork 1.13.0 allows the administrator with appropriate permissions to modify an existing subnet if the DHCP servers associated with this subnet have the subnet_cmds hook library installed and loaded. Stork currently doesn’t support modifying the subnet pools.
The Assignments multi-select can be used to associate the subnet with new servers or remove a subnet from the existing servers.
All DHCP parameters except relay configuration can be modified in the form. Typically, the same values are specified and populated to all the DHCP servers. However, it is possible to unlock selected parameters, and specify different values for different servers. In the picture below, different allocators and client classes have been specified for the servers.
Similarly, different DHCP options can be specified for different servers.
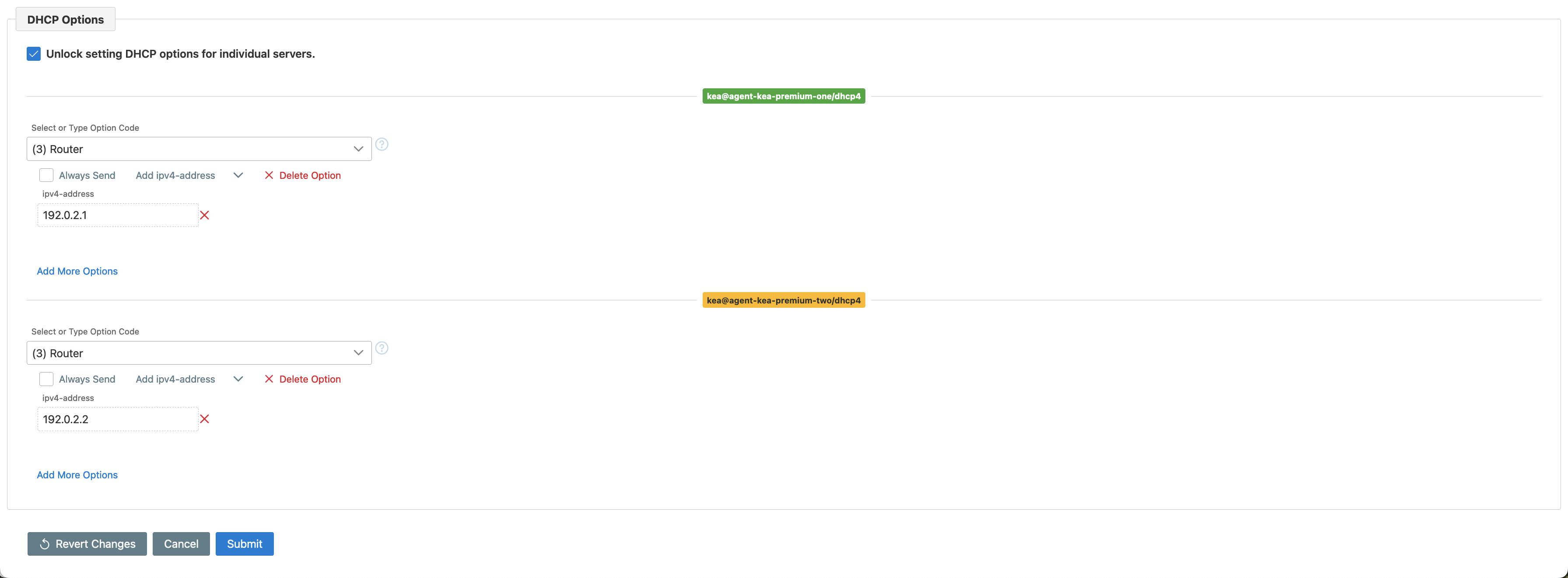
The detailed shared network view begins with listing the servers including the shared network in their configuration. It also shows all subnets belonging to the shared network.
Shared network usage statistics are shown in pie charts. A bug fix included in this release has corrected some statistics that were previously inaccurate.
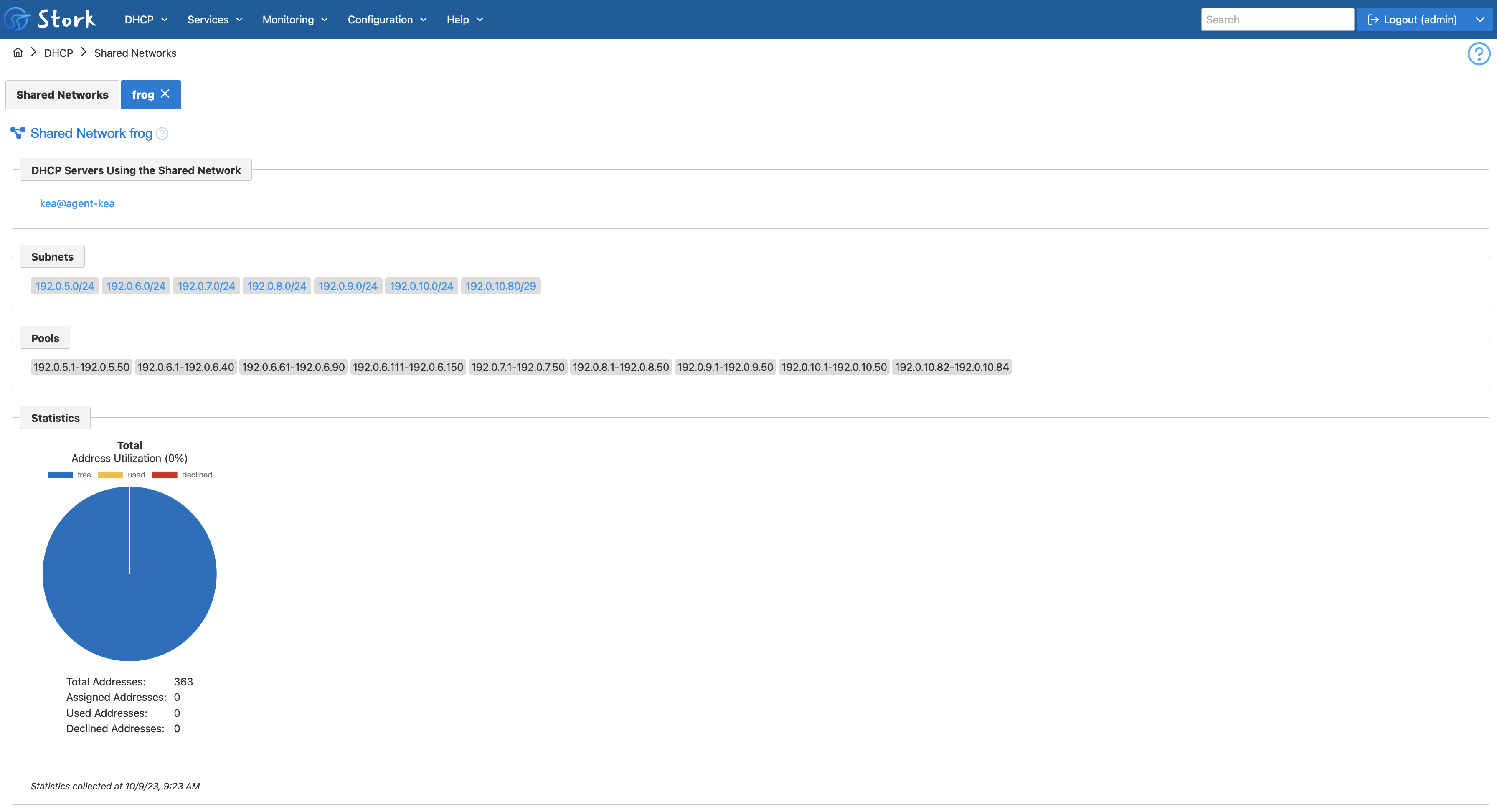
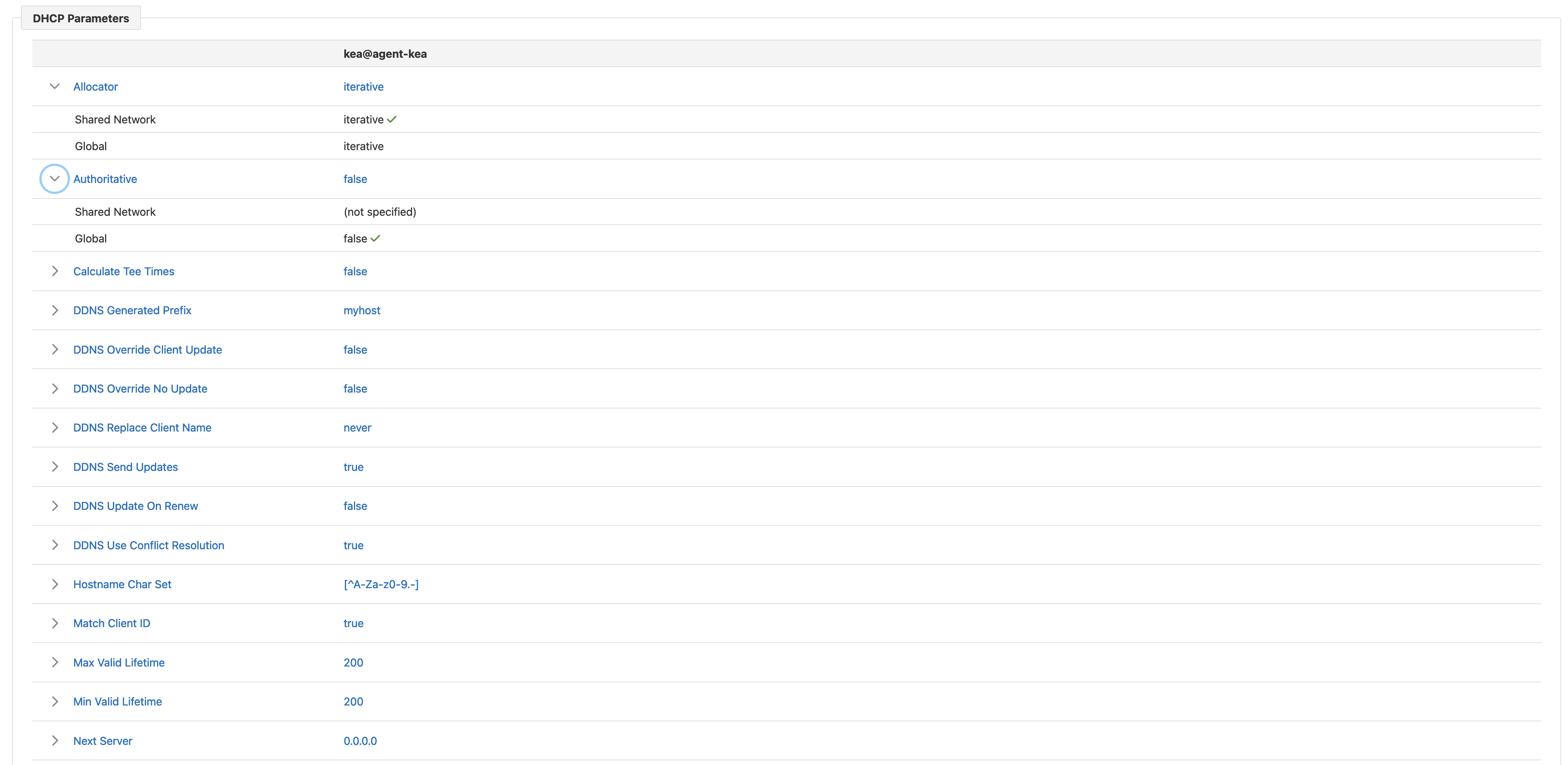
Next, there are DHCP parameters configured for the shared network in different Kea servers. The expandable rows contain the values of these parameters specified at different configuration levels (i.e., shared network and global level). The example shown includes only one Kea server, but if there were more configured, they would be displayed in additional columns. This view allows the administrator to see at a glance whether different Kea servers have different settings for the shared network.
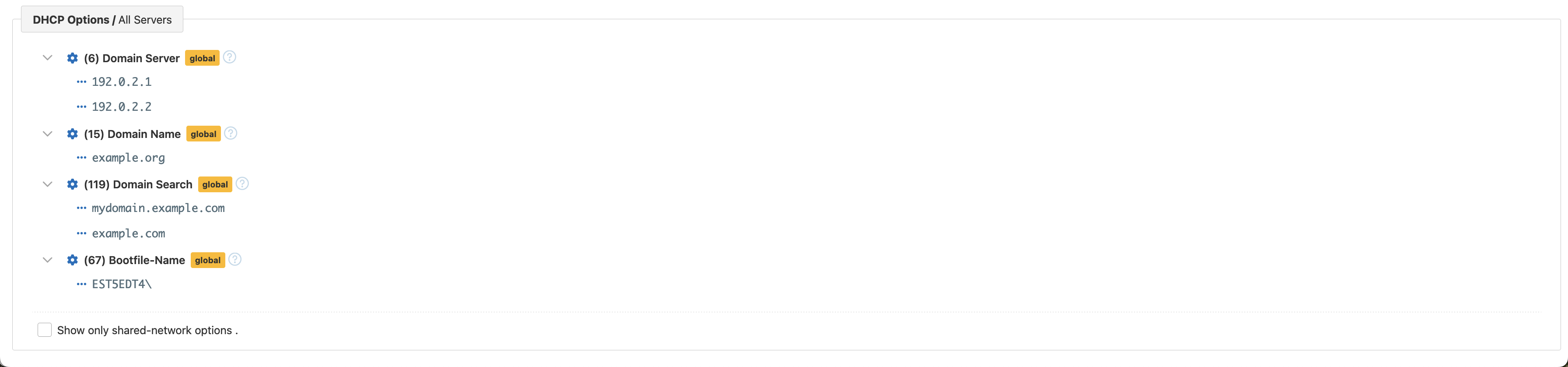
Finally, the shared network view contains DHCP options specified for the shared network at different levels (i.e., shared network and global level). The checkbox allows for filtering only shared network-level options.
The ability to link optional libraries has been a popular and successful feature for Kea. Stork now has its first hook library, to provide Stork user authentication via LDAP. This feature has been in development for several months, as it required implementation of some infrastructure for loading external libraries, but it is now ready for use.
We have based our LDAP integration on the go-ldap library. Because we didn’t have much in the way of detailed user requirements for LDAP, we had a lively discussion both on and off our open Stork GitLab repository about requirements, user preferences, and defaults. It is now possible to designate LDAP as the authentication method for some or all users, although an individual user must be configured to authenticate via one mechanism or the other.
Stork 1.13.0 includes support for reading the user group or role from LDAP and mapping that to a Stork user group for authorization purposes. For example, it is possible to limit access to Stork to users included in a specific group in the LDAP directory. The current release does not support creating or managing user roles in Stork from LDAP, so if you have a user group in LDAP that you want to assign Stork privileges to, you must create a corresponding user group in Stork to implement that. By default, Stork maps the stork-admin LDAP group to the admin role in Stork and the stork-super-admin group to the super-admin role in Stork. These groups may be overridden if needed.
What's New from ISC